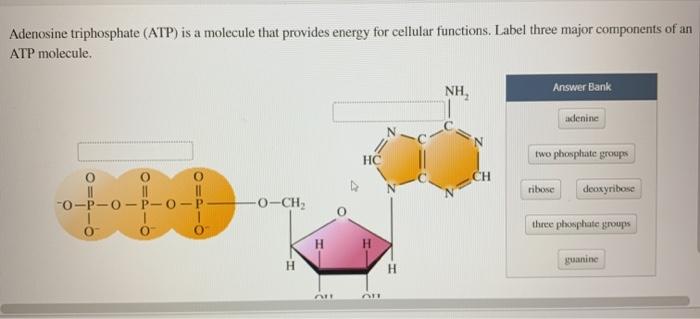
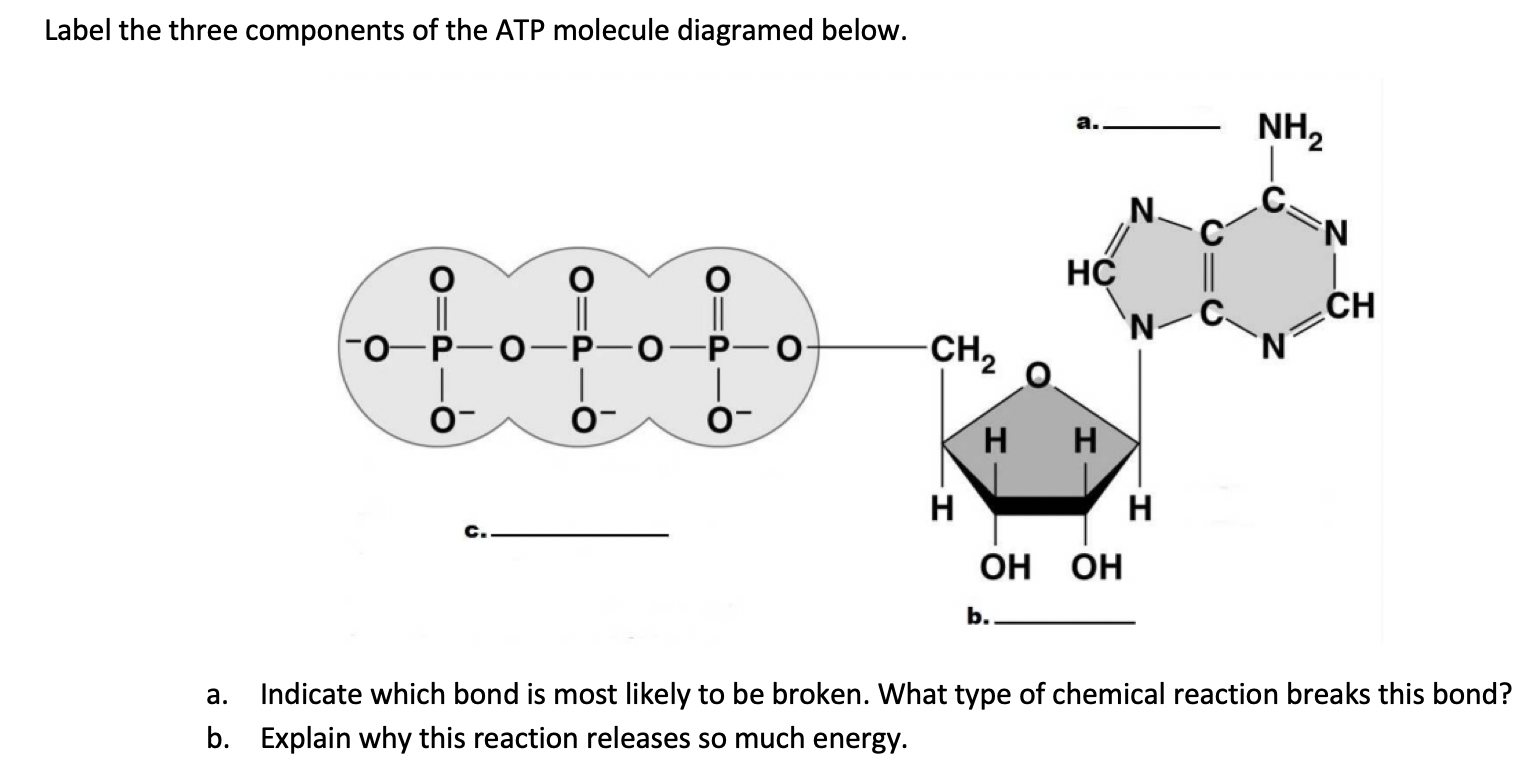
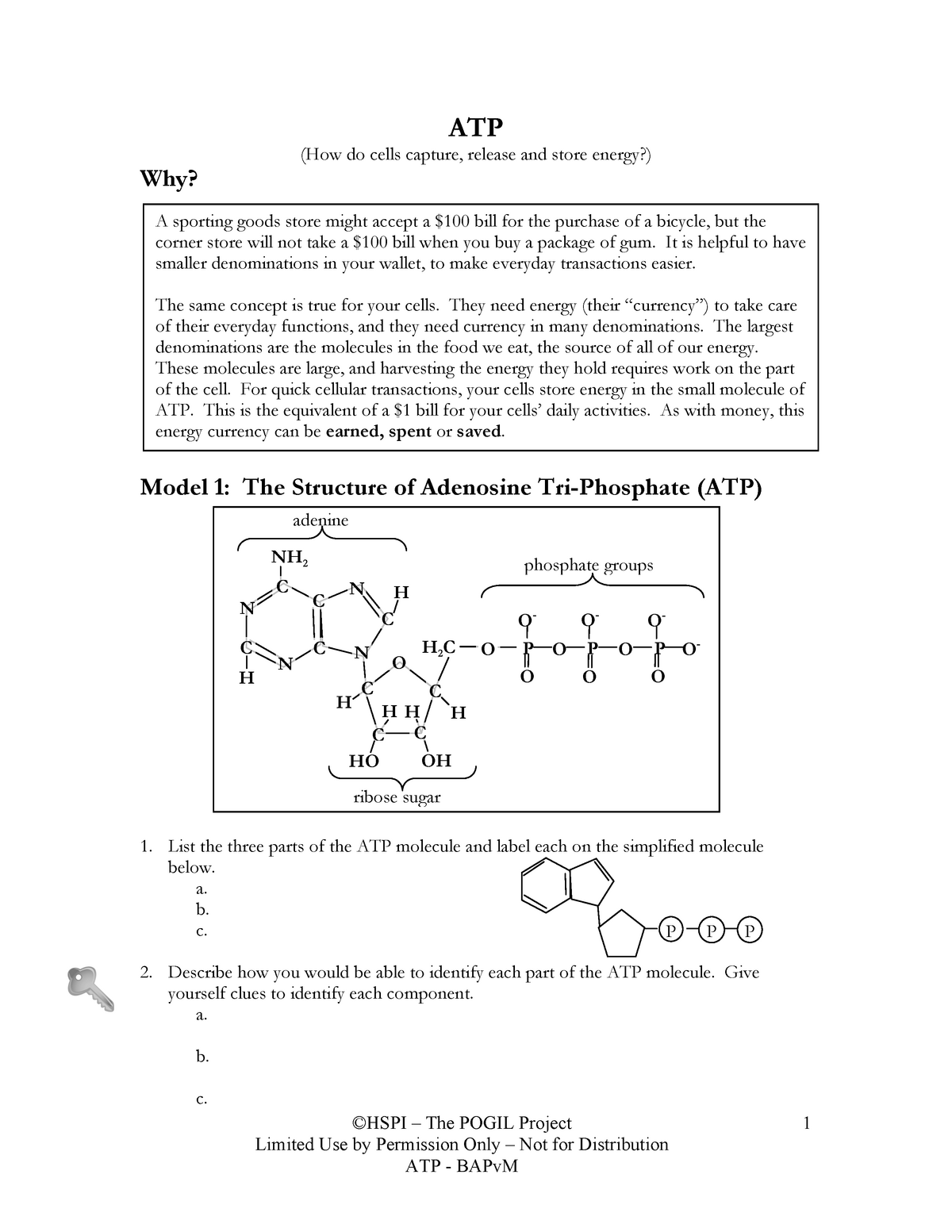
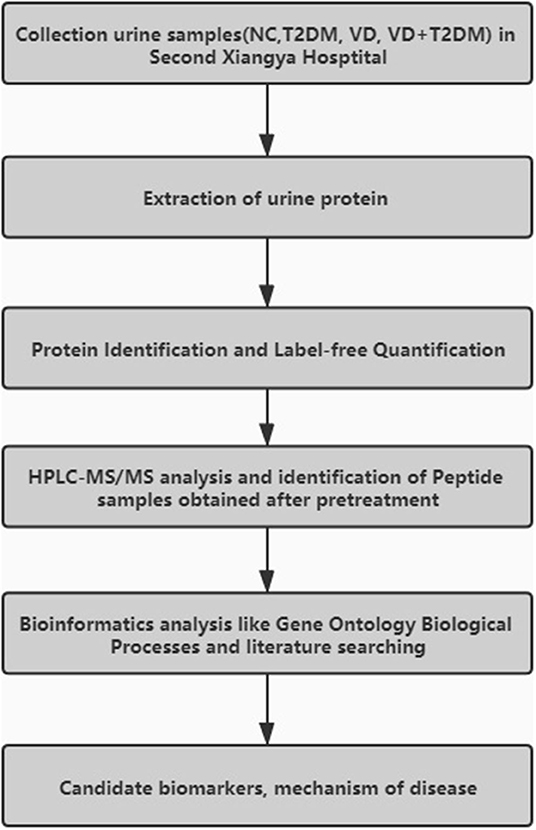
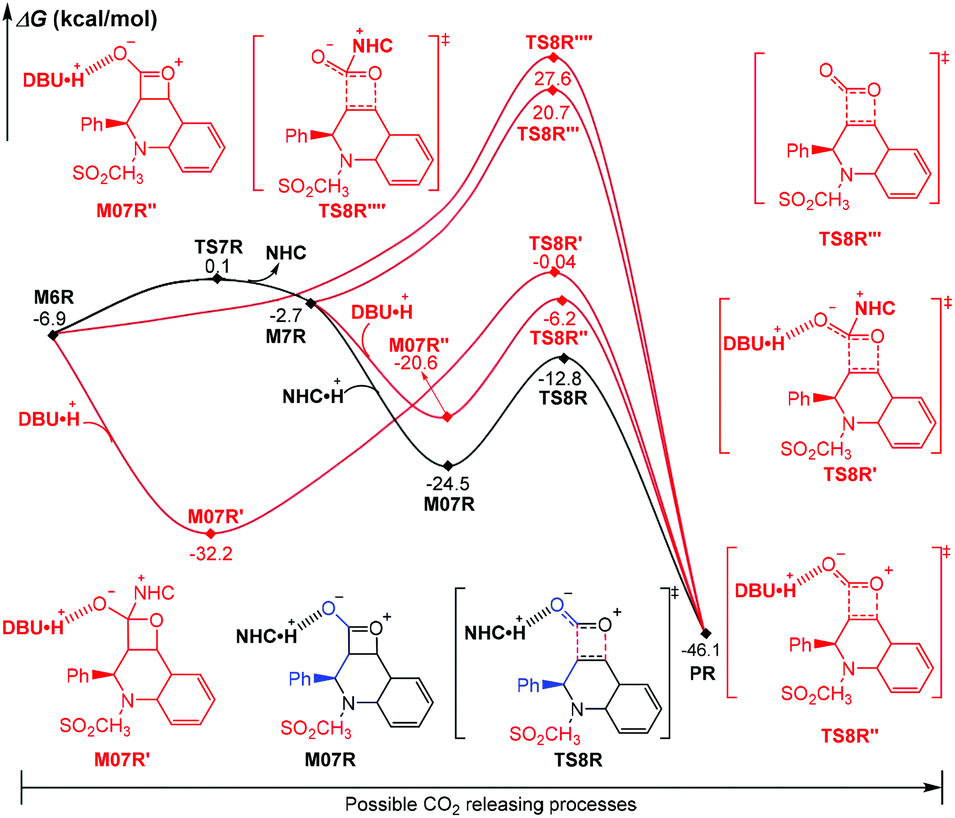
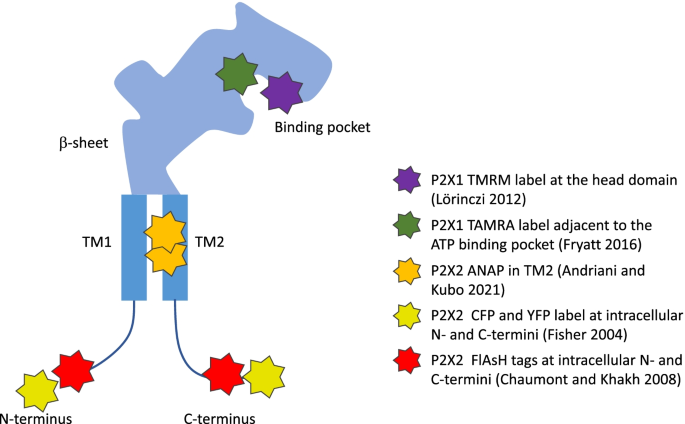
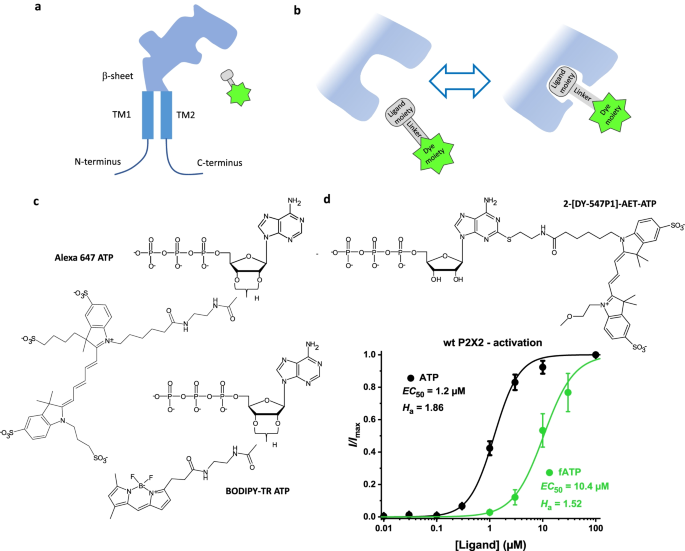
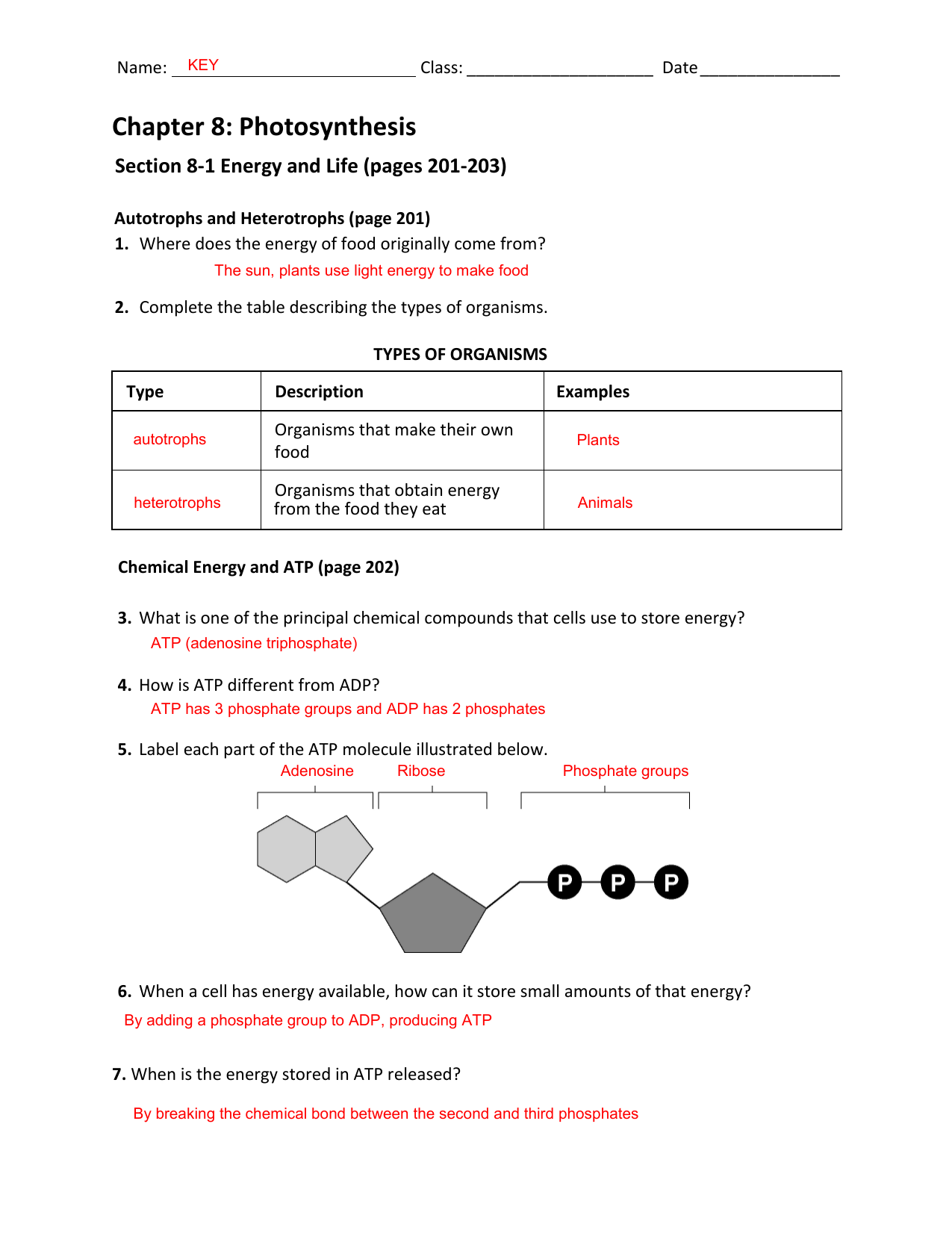
43 label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below.
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams May range from 34 to 38 net ATP. The above cellular respiration formula is formulated by combining the three following processes into a single one. Such processes are explained below. Stages of Cellular Respiration 1. Glycolysis Diagrammatic illustration of the Cellular Respiration Pathway (Source: Slide Share) Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The ATP molecule is composed of three components. These phosphates are the key to the activity of ATP. ATP consists of a base, in this case adenine (red), a ribose (magenta) and a phosphate chain (blue). All living things, plants and animals, require a continual supply of energy in order to function.
PDF ATP - Loudoun County Public Schools ATP (How do cells capture, release and store energy?) Why? Model 1: The Structure of Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) 1. List the three parts of the ATP molecule and label each on the simplified molecule below. a. b. c. 2. Describe how you would be able to identify each part of the ATP molecule. Give yourself clues to identify each component. a. b. c.

Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below.
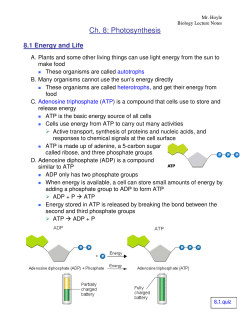
PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life - dps61.org 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples Autotrophs Organisms that make their own food Plants Heterotrophs Organisms that obtain energy from Animals, mushrooms the food they eat Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups P P P 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. What is atp an abbreviation for. n V (Ed. [6] Helicases may process much faster in vivo than in vitro due to the presence of accessory proteins that aid in the destabilization of the fork junction. Answered: Part 1: The structure of ATP TP… | bartleby Part 1: The structure of ATP TP consists of 3 parts: I adenine molecule, I ribose sugar molecule, and 3 phosphate molecules. nergy is stored in the bond that is found between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. 1. COLOR the following ATP molecules below and provide a key to show the 3 parts. 2. Label the area that represents the HIGH ENERGY bond.
Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below.. PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) - Mystr Nakashima Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat P P P TYPES OF ORGANISMS Chemical Energy and ATP(page 202) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) - Biology || Miss B Chemical Energy and ATP (page 202) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? 7. When is the energy stored in ATP released? Photosynthesis: ATP and ADP Cycle - bealsscience ATP is one of the most important compounds inside a cell because it is the energy transport molecule. ATP (Adenosine TriPhosphate) is considered a transporter of energy because when one of the phosphate groups is broken off, turning it into Adenosine DiPhosphate (the Tri means 3 phosphate groups, the Di means 2 phosphate groups). DOC 013368718X_CH08_115-128.indd (ATP). Ribose is a 5-carbon sugar molecule that is part of an ATP molecule. The phosphate groups of ATP are the key to its ability to store and supply energy. ATP releases energy when it breaks bonds between its phosphate groups. Most cells only store enough ATP for a few seconds of activity.
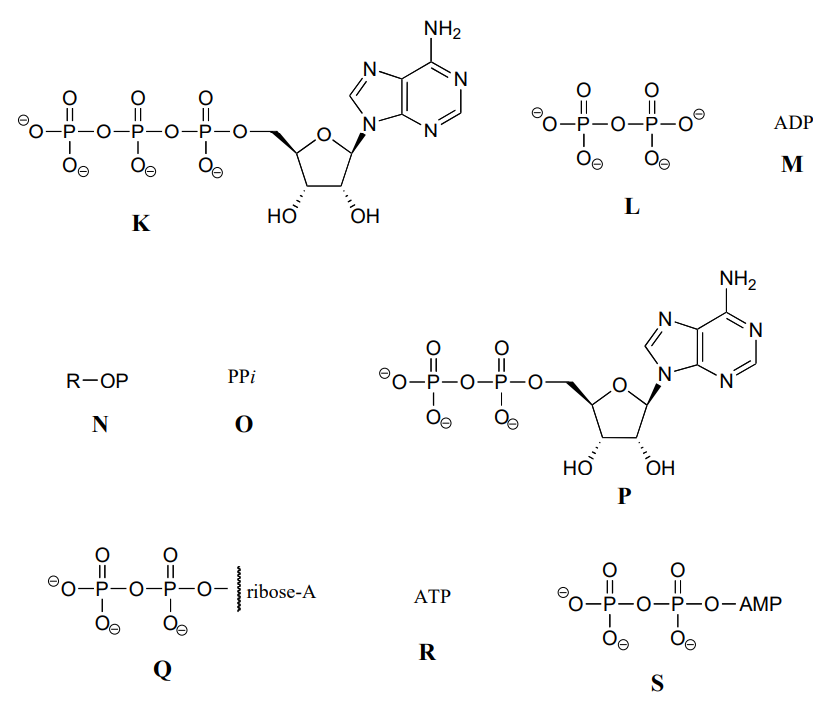
Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing - Chegg Science Biology Biology questions and answers 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. Explain why glucose is important. groups groups 4. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 5. What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture: Answer link. ATP AND BIOLOGICAL ENERGY - Estrella Mountain Community College How to Make ATP | Back to Top. Two processes convert ADP into ATP: 1) substrate-level phosphorylation; and 2) chemiosmosis. Substrate-level phosphorylation occurs in the cytoplasm when an enzyme attaches a third phosphate to the ADP (both ADP and the phosphates are the substrates on which the enzyme acts). This is illustrated in Figure 3. Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers Adenine, Ribose, and the Triphosphate moiety.The parts of a molecule of ATP are:the purine base, hydrogen;linked to the sugar, glucose;linked to a chain of ten phosphate groups.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis, TE - Scarsdale Public Schools ATP has three phosphate groups, while ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples Autotrophs Organisms that make their own food Plants Heterotrophs Organisms that obtain energy from Animals, mushrooms the food they eat Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups P P P 6. Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule - Chegg Transcribed image text: Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions &-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low battery? What arc two ways in which the diagram shows an increase in energy? Describe the concepts shown in the diagram. PDF Worksheet: Photosynthesis & Cell Energy - SC TRITON Science Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 13. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? 14. When is the energy stored in ATP released? 15. What are three factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs?
PDF Scarsdale Public Schools / Overview 4. How is ATP different from ADP? ATP has three Phosphate groups, while ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups p p 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? It can add a phosphate group to ADP molecules, producing ATP molecules. 7.
A&p test 2 Flashcards | Quizlet What is the function of ATP molecules in living cells? Multiple Choice-They are an integral part of the cell membrane, important in transporting water molecules.-They capture energy from the oxidation of fuels in their high-energy phosphate bonds, and the energy is used in various cell processes.-They form a genetic material.
Answered: Part 1: The structure of ATP TP… | bartleby Part 1: The structure of ATP TP consists of 3 parts: I adenine molecule, I ribose sugar molecule, and 3 phosphate molecules. nergy is stored in the bond that is found between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. 1. COLOR the following ATP molecules below and provide a key to show the 3 parts. 2. Label the area that represents the HIGH ENERGY bond.
atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. What is atp an abbreviation for. n V (Ed. [6] Helicases may process much faster in vivo than in vitro due to the presence of accessory proteins that aid in the destabilization of the fork junction.
PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life - dps61.org 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples Autotrophs Organisms that make their own food Plants Heterotrophs Organisms that obtain energy from Animals, mushrooms the food they eat Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups P P P 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy?











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)










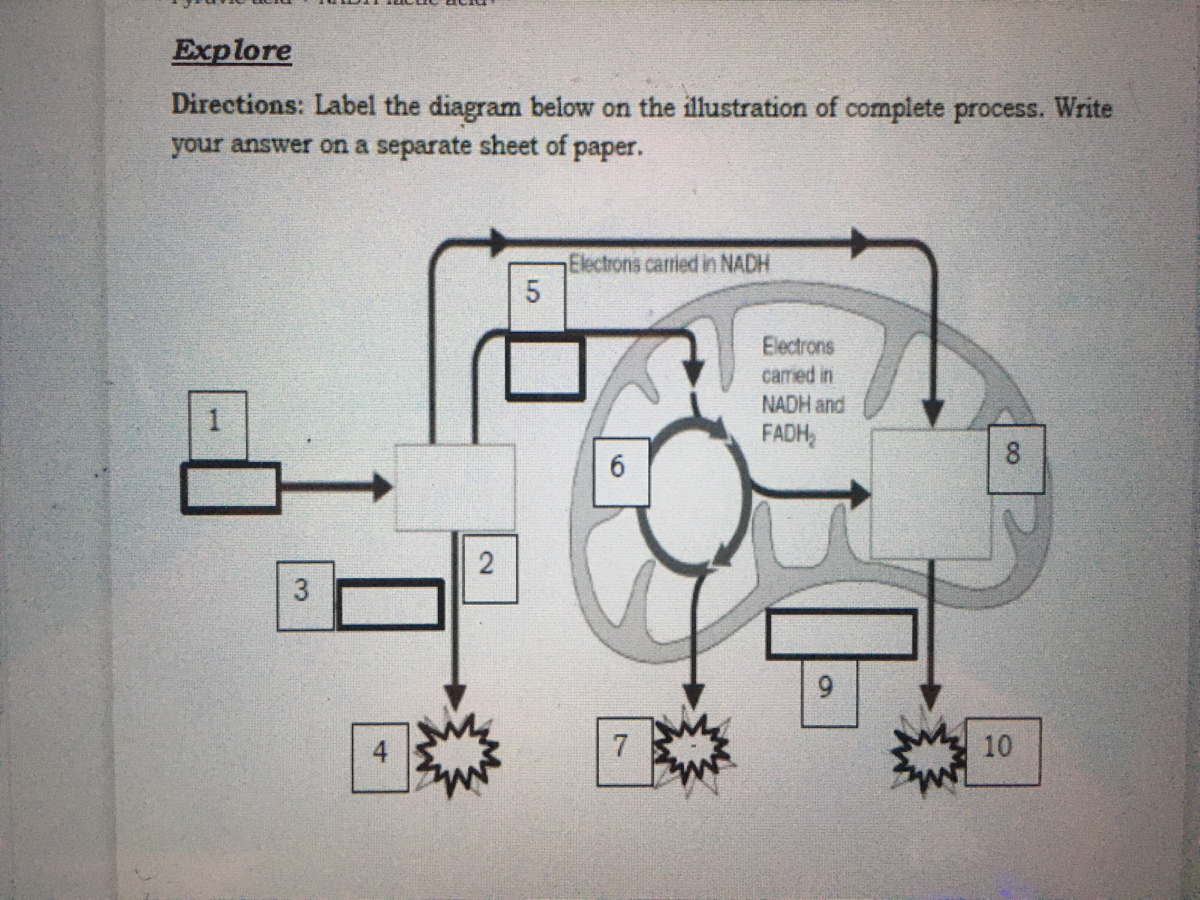

Post a Comment for "43 label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below."